
| Main Page | Capacitance | Cursos |
 |
Neil C. Bruce | ||||
|
Design and construction of a polarimetric scatterometer for 2D surfaces
We are currently building a scanning scatterometer to measure the polarised scattered light from a 2D rough surface. This type of surface scatters light into a hemisphere above the surface, and not a plane as is the case for a 1D rough surface (see the figure below).
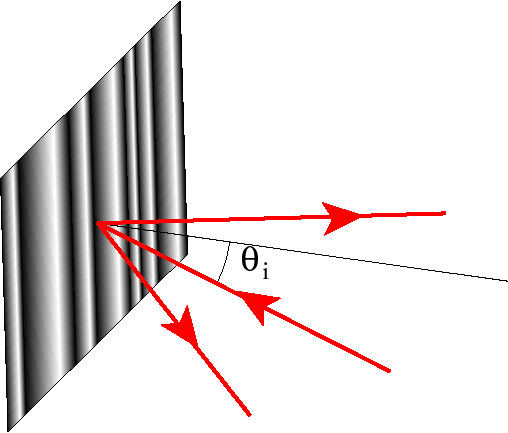 |
A 1D surface scatters light into a plane |
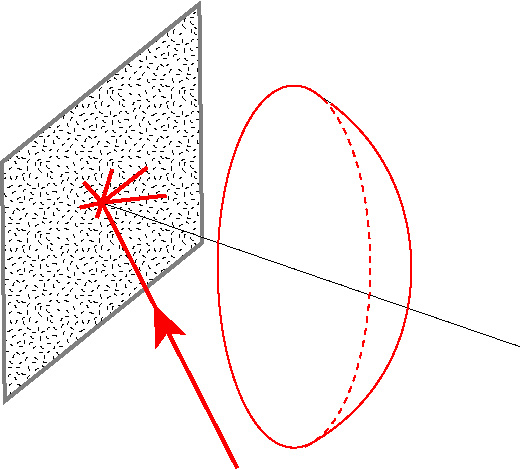 |
A 2D surface scatters light into a hemisphere above the mean plane of the surface |
There are two types of scatterometers that can be built: a mirror scatterometer (like the one we have built) which uses optical elements to collect the scattered light and direct it to a detector, which is usually a CCD camera; and a scanning type of scatterometer which scans a detector over the area of interest. This proyect involves the design and construction of a scanning-type scatterometer to cover the full hemisphere to measure the scattered light from a 2D rough surface. The figure below shows the general design of the scatterometer.
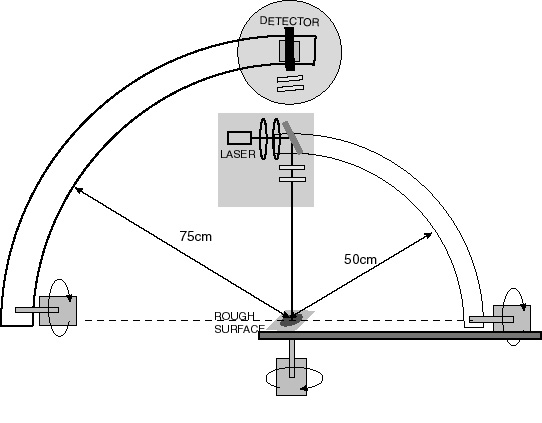
The incident and scatter angles are controlled by two rotational
motors and a third motor rotates the laser/surface assembly to cover the full
hemisphere of scattered light. The system has been designed with a maximum
resolution of 0.25°.