
| Main Page |
|
Capacitance |
|
Polarization | Cursos |
 |
Neil C. Bruce | |||||
|
The
characterization of rough surfaces using capacitance measurements.
It is possible to characterize rough surfaces using measurements of the capacitance between the rough surface and a known electrode. The known electrode can be plane or can have a controlled structure.
The figure shows the effect of changing the separation between a perfectly conducting planar electrode and a perfectly conducting Gaussian rough surface (Gaussian distribution of heights and Gaussian correlation length) for surfaces with different standard deviations of the heights (top graph) and different correlation lengths (bottom graph).
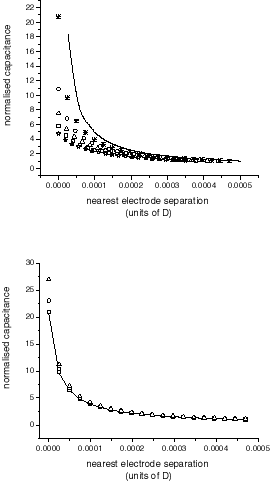
It can be seen that the capacitance depends on the standard deviation of the rough surface structure but is independent of the correlation length. This means that, with a suitable calibration, the standard deviation of the rough surface height could be measured by fitting the capacitance as a function of the electrode separation.
The lateral structure, in this case the correlation length can be measured with a shaped electrode, in particular an electrode with a pointer superimposed on a planar base. Results for this case are shown in the figure below.
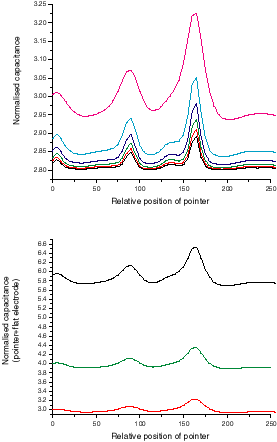
In this figure the variation of capacitance while scanning a pointer over the rough surface is shown. In the top graph different curves are for different correlation lengths and in the bottom graph the curves are for different standard deviations of the height.
It can be seen that the average capacitance of the scanned pointer, which could be measured with a single flat electrode with many pointers superimposed, depends on both the correlation length and the standard deviation of the heights. Therefore this measurement permits the calculation of the correlation length of the rough surface.
Publications:
| ICAT |